#Linux Integration Services Version 4.1 for Hyper-V
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=51612
New with Linux Integration Services 4.1:
•Expanded Releases: now applicable to Red Hat Enterprise Linux, CentOS, and Oracle Linux with Red Hat Compatible Kernel versions 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, and 7.2.
•Hyper-V Sockets.
•Manual Memory Hot Add.
•SCSI WNN.
•lsvmbus.
•Uninstallation scripts.
When installed in a supported Linux virtual machine running on Hyper-V, the Linux Integration Services provide:
•Driver support: Linux Integration Services supports the network controller and the IDE and SCSI storage controllers that were developed specifically for Hyper-V.
•Fastpath Boot Support for Hyper-V: Boot devices now take advantage of the block Virtualization Service Client (VSC) to provide enhanced performance.
•Time Keeping: The clock inside the virtual machine will remain accurate by synchronizing to the clock on the virtualization server via Timesync service, and with the help of the pluggable time source device.
•Integrated Shutdown: Virtual machines running Linux can be shut down from either Hyper-V Manager or System Center Virtual Machine Manager by using the “Shut down” command.
•Symmetric Multi-Processing (SMP) Support: Supported Linux distributions can use multiple virtual processors per virtual machine. The actual number of virtual processors that can be allocated to a virtual machine is only limited by the underlying hypervisor.
•Heartbeat: This feature allows the virtualization server to detect whether the virtual machine is running and responsive.
•KVP (Key Value Pair) Exchange: Information about the running Linux virtual machine can be obtained by using the Key Value Pair exchange functionality on the Windows Server 2008 virtualization server.
•Integrated Mouse Support: Linux Integration Services provides full mouse support for Linux guest virtual machines.
•Live Migration: Linux virtual machines can undergo live migration for load balancing purposes.
•Jumbo Frames: Linux virtual machines can be configured to use Ethernet frames with more than 1500 bytes of payload.
•VLAN tagging and trunking: Administrators can attach single or multiple VLAN ids to synthetic network adapters.
•Static IP Injection: Allows migration of Linux virtual machines with static IP addresses.
•Linux VHDX resize: Allows dynamic resizing of VHDX storage attached to a Linux virtual machine.
•Synthetic Fibre Channel Support: Linux virtual machines can natively access high performance SAN networks.
•Live Linux virtual machine backup support: Facilitates zero downtime backup of running Linux virtual machines.
•Dynamic memory ballooning support: Improves Linux virtual machine density for a given Hyper-V host.
•Synthetic video device support: Provides improved graphics performance for Linux virtual machines.
•PAE kernel support: Provides drivers that are compatible with PAE enabled Linux virtual machines.
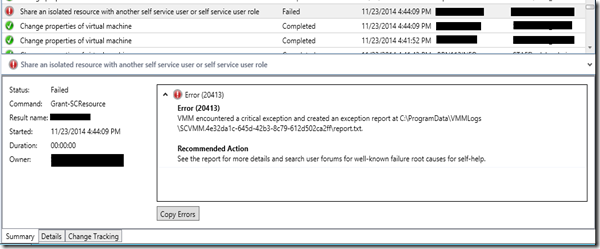
VMM Tips & Tricks: Add VM to User Role job fails with Error 20413
In New VMM 2012 R2 with CU3 implementation when you try to add VM to existing user role you may see below error
Error (20413)
VMM encountered a critical exception and created an exception report at C:\ProgramData\VMMLogs\SCVMM.4e32da1c-645d-42b3-8c79-612d502ca2ff\report.txt.
Recommended Action
See the report for more details and search user forums for well-known failure root causes for self-help.
After some investigation I found the error related to VMM DB, After applying the CU3 you need to run same SQL script described in CU1, CU2
Important After you install the update package, you must apply the following SQL script on your Virtual Machine Manager Microsoft SQL Server database for Update Rollup 2 to function correctly.
https://support.microsoft.com/kb/2932926?wa=wsignin1.0
Please make sure to have a backup from VMM DB before any modification to it. Once script run successfully the VM can be added to user role without any issue
System Center Service Manager :A Windows Workflow Foundation workflow failed during execution.
Sometimes when you check the event viewer for Service Manager “Operations Manager” you get event ID 33880
A Windows Workflow Foundation workflow failed during execution.
Workflow Type: Microsoft.EnterpriseManagement.ServiceManager.SLA.Workflows.ApplySLAOnGroupInstanceWorkflow Identifier: b3c0e6b3-b14e-345b-0cdc-cb6feaa9e3cd
Exception Type: Microsoft.EnterpriseManagement.Common.InconsistentDataException
Exception Message: Could not retrieve SLO information from the system. This can happen when SLO was either deleted or not created through console.
Exception Stack: at Microsoft.EnterpriseManagement.ServiceManager.SLA.Workflows.ApplySLAOnGroupInstance.ApplySLA_ExecuteCode(Object sender, EventArgs e)
at System.Workflow.ComponentModel.Activity.RaiseEvent(DependencyProperty dependencyEvent, Object sender, EventArgs e)
at System.Workflow.Activities.CodeActivity.Execute(ActivityExecutionContext executionContext)
at System.Workflow.ComponentModel.ActivityExecutor`1.Execute(T activity, ActivityExecutionContext executionContext)
at System.Workflow.ComponentModel.ActivityExecutorOperation.Run(IWorkflowCoreRuntime workflowCoreRuntime)
at System.Workflow.Runtime.Scheduler.Run()
This happens due to missing Workflow in one of the management packs, To correct that you have to get the workflow and remove it
to get the workflow using identifier you can open SM powershell and run
get-scsmworkflow -id <WorkflowID>
if the workflow does not exist in the SM console or if you would like to force deleting it then run:
get-scsmworkflow -id <WorkflowID> | remove-scsmworkflow
Linux Integration Services Version 3.5 for Hyper-V
Hyper-V supports both emulated (“legacy”) and Hyper-V-specific (“synthetic”) devices for Linux virtual machines. When a Linux virtual machine is running with emulated devices, no additional software is required to be installed. However, emulated devices do not provide high performance and cannot leverage the rich virtual machine management infrastructure that the Hyper-V technology offers. To make full use of all benefits that Hyper-V provides, it is best to use Hyper-Vspecific devices for Linux. The collection of drivers that are required to run Hyper-V-specific devices is known as Linux Integration Services (LIS).
For certain older Linux distributions, Microsoft provides an ISO file containing installable LIS drivers for Linux virtual machines. For newer Linux distributions, LIS is built into the Linux operating system, and no separate download or installation is required. This guide discusses the installation and functionality of LIS drivers on older Linux distributions.
Blow are the main Points that comes with version 3.5
New OS with 3.5
Expands the list of supported distributions to include RHEL/CentOS 5.5-5.6.
Supported Virtualization Server Operating Systems
This version of Linux Integration Services (LIS) supports the following versions of Hyper-V:
Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard, Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise, and Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter
Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2008 R2
Windows 8 Pro
Windows 8.1 Pro
Windows Server 2012
Windows Server 2012 R2
Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2012
Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2012 R2
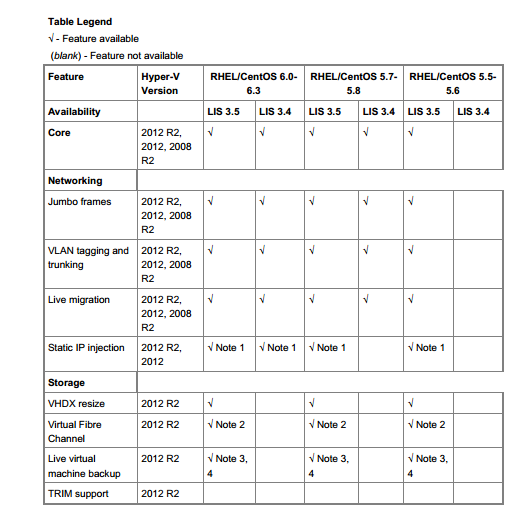
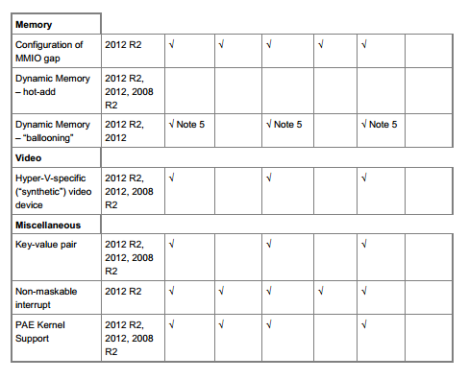
When installed on a virtual machine that is running a supported Linux distribution, LIS 3.5 for Hyper-V provides the functionality listed in the table below. For comparative purposes, hereunder also list the features available in LIS 3.4. This allows users to decide if they want to upgrade from LIS 3.4 to LIS 3.5.
Notes
1. Static IP injection might not work if Network Manager has been configured for a given HyperV-specific network adapter on the virtual machine. To ensure smooth functioning of static IP injection, ensure that either Network Manager is turned off completely, or has been turned off for a specific network adapter through its Ifcfg-ethX file.
2. When you use Virtual Fibre Channel devices, ensure that logical unit number 0 (LUN 0) has been populated. If LUN 0 has not been populated, a Linux virtual machine might not be able to mount Virtual Fibre Channel devices natively.
3. If there are open file handles during a live virtual machine backup operation, the backed-up virtual hard disks (VHDs) might have to undergo a file system consistency check (fsck) when restored.
4. Live backup operations can fail silently if the virtual machine has an attached iSC SI device or a physical disk that is directly attached to a virtual machine (“pass-through disk”).
5. LIS 3.5 only provides Dynamic Memory ballooning support—it does not provide hot-add support. In such a scenario, the Dynamic Memory feature can be used by setting the Startup memory parameter to a value which is equal to the Maximum memory parameter. This results in all the requisite memory being allocated to the virtual machine at boot time—and then later, depending upon the memory requirements of the host, Hyper-V can freely reclaim any memory from the guest. Also, ensure that Startup Memory and Minimum Memory are not configured below distribution recommended values.
SCCM and FEP support for Windows Azure Virtual Machines
Microsoft just release new KB regarding support for System Center 2012 Configuration Manager and System Center 2012 Endpoint Protection support for Windows Azure Virtual Machines.
System Center 2012 Configuration Manager Service Pack 1 (SP1) or later versions and System Center 2012 Endpoint Protection SP1 or later versions support two specific scenarios to manage server software in the Windows Azure Virtual Machine environment.
The following table lists the scenarios and supported Configuration Manager features in each scenario.
|
Supported scenarios |
Supported Configuration Manager features |
|
Use an existing on-premises Configuration Manager infrastructure to manage Windows Azure Virtual Machines that are running Windows Server or Linux through a secure site-to-Site connection. |
For Windows Server:
For Linux:
|
|
Set up a single stand-alone Primary site in the Windows Azure Virtual Machines environment to manage Windows Azure Virtual Machines that are running Windows Server or Linux in the same virtual network. |
For Windows Server:
For Linux:
|
The following Linux distributions are endorsed for Windows Azure Virtual Machines in the supported scenarios:
- Canonical Ubuntu 12.04
- OpenLogic CentOS 6.3
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP2
Note The Linux-based virtual machines must be running version 1.0.0.4648 or later versions of the Linux client for Configuration Manager.
System Center Operations Manager: Windows Server 2012 R2 MPs *Updated*
Last Update: 25-10-2013
With official release of Windows 2012 R2 and System Center 2012 R2 Microsoft provided new MPs for new OS. This is a quick list that will be updated with new MPs
This management pack is supported to run in System Center 2012 Operations Manager, System Center 2012 Operations Manager SP1, and System Center 2012 Operations Manager R2.
|
Management Pack |
URL |
| System Center Management Pack for Windows Server Operating System | http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=9296 |
| System Center Management Pack for Windows Server 2012 R2 Hyper-V | http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=40798 |
| System Center Management Pack for Windows Server Cluster | http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=2268 |
| System Center Management Pack for WSUS on Windows Server 2012 R2 | http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=40801 |
| System Center Management Pack for Windows Server DNS | http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=37141 |
| System Center 2012 Management Pack for Windows Server 2012 R2 Windows Deployment Services | http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=40800 |
| System Center Management Pack for Windows Server Network Load Balancing | http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=13302 |
| System Center Management Pack for Windows Print Server 2012 R2 | http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=40804 |
| Active Directory Domain Services Management Pack for System Center | http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=21357 |
| System Center Management Pack for Windows Server 2012 R2 DHCP | http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=39062 |
| System Center 2012 Management Pack for Microsoft Windows Server AD CS 2012 R2 | http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=34765 |
| System Center 2012 Management Pack for Windows Server 2012 R2 Remote Access | http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=40802 |
| System Center Management Pack for Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials | http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=40809 |
| System Center 2012 Management Pack for Multi-Tenant RemoteAccess 2012 | http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=40807 |
| System Center 2012 Management Pack for Microsoft Windows Server 2012 Internet Information Service 8 | http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=34767 |
System Center Configuration Manager Company Portal App
The System Center Configuration Manager Company Portal app allows users of Windows 8 and Windows 8.1 machines to view and install applications made available to the user by their administrators. The machine must be managed by Microsoft System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager, or later, with the agent installed.
The app communicates directly with the Configuration Manager on-premise server infrastructure. Note that this contrasts with the Windows Intune Company Portal app (available through the Windows Store and the Download Center) which communicates directly with the Windows Intune service.
You can download from http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=40795&WT.mc_id=rss_alldownloads_all
Requirements
- Administrative
- System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager
- The Application Catalog Web Service and Application Catalog Website Point roles must be operational on one or more primary sites
- End User Machines
- Windows 8 Pro, Windows 8 Enterprise, Windows 8.1 Pro or Windows 8.1 Enterprise
- Machine must be domain-joined
- System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager (or later) client agent must be installed
- User must be logged on with domain credentials
Installation
To enable Company Portal app functionality a registry key must be present on target devices. This allows the Configuration Manager agent to communicate with the Company Portal app. The required value is:
- Key = [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\CCM]
- Value Name = PortalPackageFamily
- Type = REG_SZ
- Value = Microsoft.CorporateAppCenter_8wekyb3d8bbwe
To deploy the Company Portal app, use the following steps:
- Ensure that the Application Catalog role is operational on one or more primary sites. For more information, refer to the following TechNet article: Configuring the Application Catalog and Software Center in Configuration Manager (http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=247211).
- Deploy the registry value specified above to all clients on which the Company Portal app will be installed. This can be done via Group Policy, the Compliance Settings feature of Configuration Manager, or any other method applicable in your organization.
- Deploy the Company Portal app. You can deploy this app to Windows 8 or Windows 8.1 workstations through the Application Management feature. For more information, refer to the following TechNet article: Introduction to Application Management in Configuration Manager (http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=247184) and select “Windows app package (*.appx, *.appxbundle)” in the Create Application wizard.
Note: The Company Portal app may take up to 15 minutes after installation before it is fully operational
Recommendations and Best Practices
Consider the following when deploying the Company Portal app in your environment.
- The Company Portal app utilizes the default Application Catalog Website Point assigned to the device when communicating with the Configuration Manager infrastructure. For more information, refer to the following TechNet article: About Client Settings in Configuration Manager (http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=252184).
- If you have multiple primary sites in a hierarchy, we strongly recommend adding a set of Application Catalog roles for each of the primary sites, and using Automatic detection to control the default Application Catalog Website Points.
- When the user browses the list of applications in the Company Portal, the app will display the applications that have been made available to the user, similar to the Configuration Manager Application Catalog functionality. The Company Portal will assess the operating system requirements specified for the deployment type of the application to determine if the application should be available for installation.
System Center 2012 R2 is RTM..So What is New ?!!!
As many of you already know System Center 2012 R2 release today and you can download from MSDN website. So this is a quick post about new features in each product
What’s New in VMM in System Center 2012 R2
What’s New in System Center 2012 R2 Operations Manager
What’s New in System Center 2012 R2 Service Manager
What’s New in System Center 2012 R2 App Controller
What’s New in System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager
What’s New in System Center 2012 R2 Orchestrator
Microsoft® SQL Server® Backup to Microsoft Windows® Azure®Tool
Microsoft SQL Server Backup to Windows Azure Tool enables backup to Windows Azure Blob Storage and encrypts and compresses SQL Server backups stored locally or in the cloud.
SQL Server 2012 and SQL Server 2014 have built in capability to back up to Windows Azure storage. The SQL Server Backup to Windows Azure tool provides the same functionality to previous versions of SQL Server. It can also be used to specify encryption and compression for your backups.
Using the 3-step wizard, you can specify a rule or set of rules that are applied to any SQL Server backup. One example of a rule could be to redirect all local backups to the specified Windows Azure storage. Another example of a rule would be to use compression or encryption for backups stored in a specific location.
Once you configure the rules, these rules are applied to SQL Server Backup files. If the rule is set to use Windows Azure storage account, the tool redirects the backups to the specified Windows Azure storage account, but leaves a stub file with metadata information to be used during restore.
Benefits:
· Support for backups to Windows Azure Storage for SQL Server versions that do not have the built-in capability. Using Windows Azure storage for your backups has several benefits off-site storage for disaster recovery, ability to access from any location, etc. For more information, see SQL Server Backup and Restore with Windows Azure.
· Encryption and Compress support for SQL Server versions that do not have the built in capability. Currently only SQL Server 2014 has encryption support, and SQL Server 2008 or later support compression during backup. SQL Server 2008 supports compression in Enterprise edition only, but for SQL Server 2008 R2 and later encryption is supported on Standard editions or higher.
Download from there
http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=40740
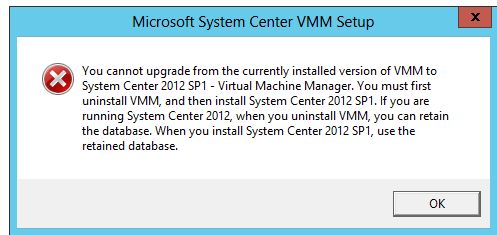
VMM Tricks: Upgrading from Currently installed of VMM to System Center VMM 2012 is Not Supported
Some times when you try to Install/upgrade VMM 2012 “ or VMM 2012 with SP1” you get the error during install of SCVMM 2012.
“you cannot upgrade from the currently installed version of VMM to system center 2012 SP1 virtual machine manager. You must first uninstall VMM, and then install SCVMM 2012 SP1. If you are running system center suite, when you uninstall VMM, you can retain the database. When you install System center 2012 SP1, use the retained database”
to uninstall Old VMM Server from your environment please follow these steps
Action Plan 1:
1.Backup new VMM SP1 instance.
2.Uninstall new VMM SP1 instance.
3.Uninstall old VMM SP1 instance.
4.Install new VMM SP1.
Action Plan 2:
To force an uninstall via command, please follow these steps:
1.Find VMServerUninstall.ini from folder Program Files\Microsoft System Center 2012\Virtual Machine Manager\setup.
2.Replace its content with following code:
[OPTIONS]
RemoteDatabaseImpersonation=0
RetainSqlDatabase=0
ForceHAVMMUninstall=1
If this VMM server’s SQL instance located on a remote server, please change the value of RemoteDatabaseImpersonation to 1.
3.Save this ini file to c:\temp.
4.Run command to locate the folder contain VMM Server setup file under command prompt: cd VMM_Setup_File_folder.
5.Run command to force uninstall VMM server:
setup.exe /server /x /f C:\Temp\VMServerUninstall.ini /SqlDBAdminDomain DomainName /SqlDBAdminName SQLAdmin /SqlDBAdminPassword password
Note: DomainName is your domina name “Like “Contoso or Fabrikum”
Account Domain\SQLAdmin is an SQL Server administrator account which is used to connect to backend SQL server.